Did you know that about 75% of American pet owners don’t know what their insurance plans don’t cover? This ignorance may result in unforeseen veterinary expenses.
Any pet owner must be aware of the exclusions from pet insurance. Certain breeds or conditions may be excluded by certain insurance, and the majority do not cover pre-existing conditions.
Knowing what your coverage does not cover is crucial for responsible pet owners to prevent unpleasant financial shocks. You may make wiser choices about your pet’s medical treatment if you are well-informed.
Typical Exclusions from Pet Insurance
Even though pet insurance may save lives, it’s important to be aware of the typical restrictions that may reduce its usefulness. Pet owners may make better judgements about their pet’s medical treatment by being aware of the restrictions that are usually included in pet insurance coverage.
Preventative and Routine Care
Routine and preventive treatment, such immunisations, dental care, and wellness checkups, are often not covered by pet insurance coverage. Although these treatments are thought to be necessary for keeping your pet healthy, most insurance policies do not cover them. It is required of pet owners to set aside money for these costs individually.
Elective surgeries and cosmetic procedures
Additionally, elective surgery and cosmetic treatments are sometimes not covered by pet insurance. This covers non-medically required cosmetic procedures including ear clipping, tail docking, and other surgery. This also applies to elective operations that are not urgently needed.
Pregnancy, Breeding, and Genetic Conditions
Pregnancy, genetic disorders, and breeding-related issues may also not be covered. Pregnancy problems, breeding expenses, and conditions passed down from the pet’s parents are all included in this. Pet owners who want to breed their animals or who are aware of possible genetic problems must comprehend these exclusions.
Pet owners may better manage the complexity of pet insurance and make sure they are ready for any out-of-pocket costs associated with their pet’s treatment by being aware of these typical exclusions.
Pre-existing Conditions: What Are Not Covered by Pet Insurance?
How pre-existing illnesses are treated is one of the most important things to know when thinking about pet insurance. Health problems that your pet develops before to applying for insurance or during the waiting period after the purchase of a policy are known as pre-existing conditions.
How Pre-existing Conditions Are Defined by Insurance Companies
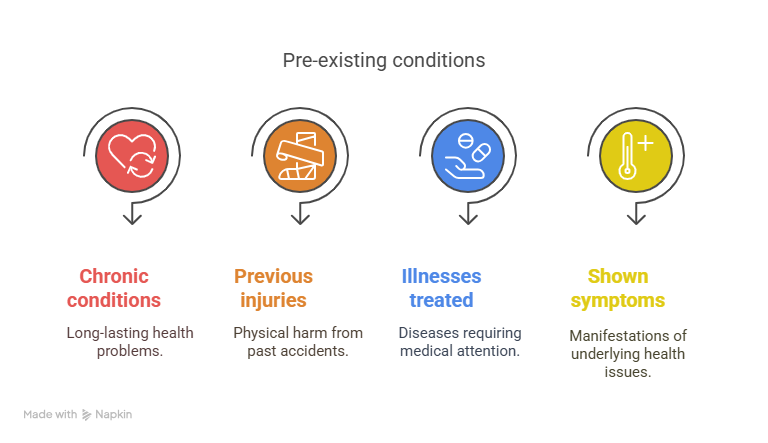
Pre-existing illnesses are generally defined by insurance carriers as any illness that manifested symptoms or was identified prior to the policy’s effective date or during the waiting period. Chronic ailments, prior injuries, and illnesses that have been treated or shown symptoms might all fall under this category.
Waiting Times and How They Affect Coverage
Waiting times are still another important factor to think about. Even if your pet hasn’t received a diagnosis yet, their ailments are often regarded as pre-existing at this period. It’s critical to comprehend the waiting time and how it impacts coverage.
| Insurance Company | Pre-existing Condition Definition | Waiting Period |
|---|---|---|
| Company A | Any condition with prior symptoms or diagnosis | 30 days |
| Company B | Conditions treated or diagnosed before coverage | 14 days |
Policy Restrictions and Limitations
Making educated judgements requires being aware of the constraints and limitations imposed by pet insurance coverage. Pet owners need to understand the different limits and exclusions that may impact their coverage.
Specific Exclusions by Breed
Breed-specific exclusions, which may restrict or eliminate coverage for certain breeds prone to particular health problems, are a feature of several pet insurance plans. For instance, because of their propensity for certain medical disorders, boxers and bulldogs may be disqualified.
Age Limitations and Senior Pet Issues
Age limitations on pet insurance coverage often impact elderly pets or dogs with pre-existing medical issues. Pets that are older may have more expensive rates or fewer alternatives for coverage.
Reimbursement Limits, Deductibles, and Coverage Caps
Policies also have reimbursement restrictions, deductibles, and coverage ceilings. For example, a policy may limit the amount of money that may be paid out each year or require pet owners to pay a deductible before their coverage begins. The amount of the veterinarian expense that is covered might also be impacted by different reimbursement restrictions.

- Recognise the restrictions of your pet insurance coverage.
- Keep in mind that some breeds are excluded.
- For older pets, think about age limits.
- Examine the reimbursement restrictions, deductibles, and coverage caps.
Conclusion: Choosing Pet Insurance With Knowledge
Making educated judgements about your pet’s coverage requires an understanding of the limitations imposed by pet insurance plans. As already said, frequent exclusions include pre-existing diseases, cosmetic operations, and regular and preventive care. Coverage may also be impacted by policy limits and restrictions, including as age restrictions and breed-specific exclusions.
It’s crucial to carefully go over the insurance specifics to make sure the provider you choose fits your pet’s requirements. You can make wise choices and provide your pet the finest care possible if you know what pet insurance does and does not cover. Think about the limitations of pet insurance plans when choosing a provider, and seek for a plan that provides extensive coverage with few exceptions.




